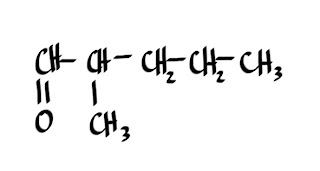We learned that a ketone is a hydrocarbon chain with a double bonded oxygen that is NOT on either end. In other words, it is an organic compound containing a C=O group at a position other than at the end of a hydrocarbon chain. The simplest ketone is propanone. As you can see, standard rules apply and we add -ONE to the parent chain.
Finally, we looked at carboxylic acids. It is an organic compound that contains a COOH group. Carboxylic acids use standard rules but change the parent chain ending to -OIC ACID. The simplest carboxylic acid is methanoic acid. They are commonly referred to as "organic acids."
 |
| Methanoic acid |
EXAMPLES:
KETONES
1.What is the structural formula for 4-octanone?
 |
| Cyclohexanone |
ALDEHYDES
1.What is the structural formula for ethanal?
 |
| Benzaldehyde |
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
1.What is the structural formula for ethanoic acid (commonly called acetic acid)?
 |
| Hexanoic acid |
Check out this cool youtube video: